Material below summarizes the article Dopamine Modulates the Activity of Sensory Hair Cells, published on December 16, 2015, in JNeurosci and authored by Cecilia Toro, Josef G. Trapani, Itallia Pacentine, Reo Maeda, Lavinia Sheets, Weike Mo, and Teresa Nicolson.
Perception of sensory stimuli, like sounds waves, is typically thought of as a unidirectional process: Sound waves hits the eardrum, and are then sensed by the inner ear, which conveys those auditory signals to the brain. At various centers of the brain, these signals are processed and relevant information is sorted. This allows for focused perception, such as hearing a particular voice among many voices.
However, there is just as much, if not more, communication that happens in the opposite direction. The brain also signals back to the ear and can influence its activity. For example, if a person is exposed to continuous loud noise, then the auditory system adapts. Consider how loud a rock concert would seem if you walked into the concert hall from a quiet room versus how loud you would perceive it to be 10 minutes later. This adaptation occurs in part by signaling from the brain to the ear.
Communication and feedback from the brain to the ear is, in most cases, not very well understood. Generally, the same signaling molecules that mediate communication among neurons in the brain are also used for signaling to the ear.
One such molecule is the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is better known for its roles in the brain’s reward system and Parkinson’s disease. Dopamine is present in the ear, but how this neurotransmitter affects cellular function and signaling has not been fully explored, partially because of the complexities of the inner ear. The inner ear expresses multiple types of dopamine receptors that signal in different ways upon binding of dopamine.
To get around this issue, we took advantage of the relatively simple system of the lateral line organ in zebrafish larvae, which is closely related to the inner ear in terms of function and cellular mechanisms.
The inner ear and lateral line are both mechanosensory organs — they respond to specific physical stimuli.
The inner ear stimulus is the movement of fluid within the cochlea or the semi-circular canals that is caused by sound waves hitting the eardrum or head movement.
The lateral line, on the other hand, is used by most aquatic vertebrates to detect the movement of external water. This is essential for vital zebrafish behaviors like schooling, predator and prey detection, and body orientation in currents. The mechanosensory cells (hair cells) of the lateral line organ are analogous to those that are employed by the ear to sense sounds and head movements. Therefore, the zebrafish lateral line organ is a good model system to study the cells and molecules that govern the senses of hearing and balance.
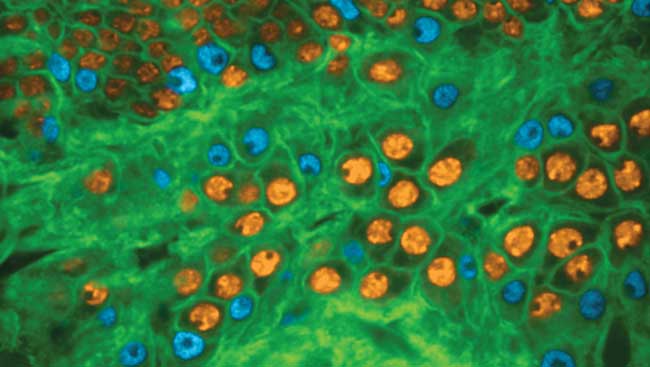
We discovered that only one type of dopamine receptor is present in the lateral line organ — the D1 receptor. We used a number of methods, including recording the charge movement through hair cells (using electrophysiology) and the concentration of calcium ions (using a sensitive imaging technique that detects fluorescence resonance energy transfer ‘FRET imaging’), to try to discern what the function of the D1 dopamine receptor is in the lateral line organ.
We observed that dopamine enhances the activity of the mechanosensory hair cells. The same mechanical stimulation produces a greater response in hair cells if dopamine receptors are activated. We know that the concentration of calcium ions is intimately linked to the ability of hair cells to send sensory signals to the brain. Therefore, we asked whether dopamine was working by increasing the movement of calcium ions into hair cells. Our calcium imaging experiments suggest that enhancement of activity depends on calcium channels that mediate calcium influx into hair cells. Finally, we looked at the shape and location of the axons that likely release dopamine in the lateral line to better understand how they might communicate with hair cells.
Our evidence suggests that a single neuron may communicate with numerous hair cells at once by releasing dopamine into the tissue surrounding multiple cells. This type of release supports the idea of dopamine exerting global control over the lateral line system, rather than fine-tuning any one hair cell’s activity. We also found that hair cells of the zebrafish inner ear express the same type of D1 dopamine receptor, suggesting that a similar mechanism is working in auditory and vestibular hair cells.
Why would enhancement of sensitivity to sound or head movements by dopamine be a useful mechanism?
The answer to this question is unknown, but the global nature of the dopamine signaling in the lateral line organ, along with the origination of these dopaminergic neurons in a particular part of the brain, suggests that this feedback system might have to do with ensuring the function or maintenance of the system (homeostasis), or that sensitivity may be affected by circadian rhythms. Perhaps having increased hearing sensitivity during the day would be an advantage for diurnal animals. Exploration of the biological function of dopamine signaling in the ear awaits further investigation.
Visit JNeurosci to read the original article and explore other content. Read other summaries of JNeurosci and eNeuro papers in the Neuronline collection SfN Journals: Research Article Summaries.
Dopamine Modulates the Activity of Sensory Hair Cells. Cecilia Toro, Josef G. Trapani, Itallia Pacentine, Reo Maeda, Lavinia Sheets, Weike Mo, Teresa Nicolson. The Journal of Neuroscience Dec 2015, 35(50): 16494-16503; DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1691-15.2015