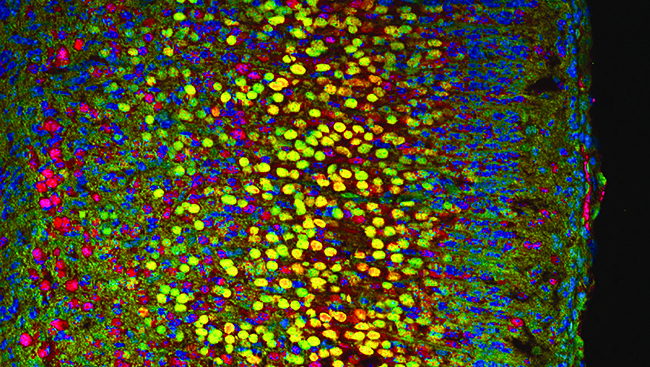
Module 1B: Functional Genomics in iPSC-Derived Neurons and Glia
In this presentation, Martin Kampmann will introduce functional genomics approaches in iPSC-derived neurons and glia. Specifically, Kampmann will:
- Cover CRISPRi (interference) and CRISPRa (activation) control of gene expression.
- Describe how to implement CRISPRi/a in iPSC-derived cells.
- Introduce large-scale genetic screens based on survival, fluorescent readouts of cell function, single-cell RNA sequencing, and high-content imaging.
- Use of functional genomics to understand mechanisms underlying disease-linked genes and potential therapeutic strategies.
Access to the full article is available to SfN members.
Neuronline is a benefit of SfN membership. Renew your membership now to make sure you don’t lose access.
Speaker

Martin Kampmann, PhD
Martin Kampmann is an assistant professor at the University of California, San Francisco Institute for Neurodegenerative Diseases and department of biochemistry and biophysics. Kampmann received his BA in biochemistry from Cambridge University, in the United Kingdom, and his PhD in biophysics and cell biology from The Rockefeller University. As a postdoctoral fellow at UCSF, he spearheaded the development of next-generation functional genomics approaches, including systematic genetic interaction maps and CRISPR-based gain- and loss-of-function screens. The goal of Kampmann’s research is to elucidate cellular mechanisms of human diseases and to develop new therapeutic strategies. For this purpose, his lab has pioneered CRISPR-based genetic screening technology in cell types derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and is investigating neurodegenerative diseases in human iPSC-derived neurons, astrocytes, and microglia.
0 of 5 articles left
Login
or
Become a Member
to unlock content