New Approach for Investigating Neuropathic Pain by Optogenetic Stimulation of Aβ Fibers
Material below summarizes the article Optogentetic Activation of Non-nociceptive Aβ Fibers Induces Neuropathic Pain-Like Sensory and Emotional Behaviors After Nerve Injury in Rats, published on February 5, 2018, in eNeuro and authored by Ryoichi Tashima, Keisuke Koga, Misuzu Sekine, Kensho Kanehisa, Yuta Kohro, Keiko Tominaga, Katsuyuki Matshushita, Hidetoshi Tozaki-Saitoh, Yugo Fukazawa, Kazuhid Inoue, Hiromu Yawo, Hidemasa Furue, and Makoto Tsuda.
Somatosensory information from the periphery is conveyed to the spinal dorsal horn (SDH) via primary afferent sensory neurons. The incoming sensory information is processed by complex circuits in the SDH, integrated to projection neurons relaying to several regions of the brain.
Primary afferents are broadly divided into two classes: nociceptive (mainly unmyelinated C, and thinly myelinated alpha delta (Aδ) fibers), and non-nociceptive (myelinated alpha beta (Aβ) fibers), which respond to noxious and innocuous stimuli, respectively.
Excitatory signals via nociceptive, which produces pain, and non-nociceptive fibers, which under normal healthy conditions do not cause pain, activate distinct SDH neuronal circuits. However, after injury to the nervous system from cancer, diabetes, chemotherapy, or trauma, even innocuous mechanical stimuli, such as the light touch of clothing, may cause pain.
This abnormal pain is known as mechanical allodynia and is a serious symptom of neuropathic pain, which is a debilitating chronic pain condition following nerve damage.
Neuropathic allodynia is refractory to the currently available treatments, including opioids. Thus, the clarification of mechanisms for neuropathic allodynia and the development of new therapeutic drugs are major challenges.
The mechanisms underlying mechanical allodynia have been investigated in rodent models of neuropathic pain. Previous studies have proposed the role of non-nociceptive Aβ fibers. However, it remains obscure.
Furthermore, it is unknown whether stimulation of non-nociceptive Aβ fibers produces allodynia-like behaviors in models of neuropathic pain. This might be due to the lack of research tools able to selectively manipulate Aβ fibers.
For elucidating the mechanistic basis of neuropathic mechanical allodynia, this study established a new approach that enables selective stimulation of non-nociceptive Aβ fibers in awake and freely moving animals using optogenetics.
We used a transgenic rat line, W-TChR2V4, within which the dorsal root ganglia (DRG)( the blue light-sensitive cation channels channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2)) are selectively expressed in innocuous mechanoreceptive A fibers, including Aβ fibers.
We applied blue laser light illumination to the plantar skin of the hind paw of W-TChR2V4 rats after peripheral nerve injury (PNI) and found that the light illumination to the PNI side of the hind paw produced pain-like behaviors of lifting and flinching.
In contrast, the illumination to the non-PNI side produced no reaction or only mild movement without any lifting or flinching. Furthermore, these light-induced neuropathic pain behaviors were resistant to morphine.
These results indicate the light illumination to the plantar surface of the hind paw of rats with PNI elicited morphine-resistant pain-like behaviors.
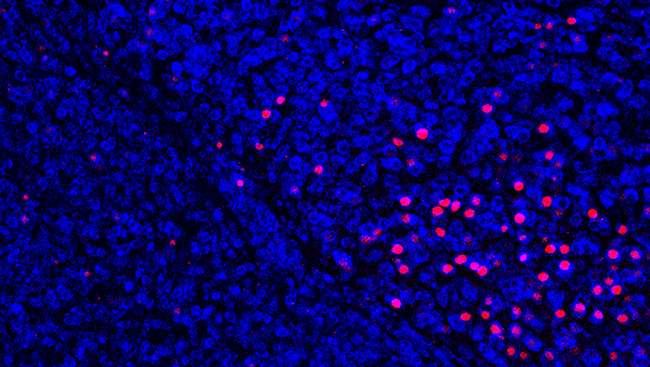
We further investigated input of optogenetically evoked signals to the SDH. In immunohistochemistry, using neuronal activity markers (c-Fos and phosphorylated ERK), we observed the number of superficial SDH neurons positive to these markers increased following light illumination to the hind paw of W-TChR2V4 rats after PNI.
Furthermore, we performed whole-cell patch-clamp recordings using spinal cord slices of W-TChR2V4 rats and investigated synaptic activity of lamina I SDH neurons (presumably nociceptive).
The optogenetic stimulation of Aβ fibers resulted in excitation of lamina I SDH neurons of PNI rats, but not naive rats. These results suggest that optically stimulated Aβ fiber signals after PNI could be conveyed to the SDH and excite lamina I SDH neurons that normally respond to noxious stimuli.
Pain has sensory and emotional aspects. Using a place-aversion apparatus, this study also demonstrates light-induced Aβ fiber stimulation after PNI induces aversive behavioral symptoms.
Furthermore, Aβ fiber stimulation activated central amygdaloid neurons, considered the core brain region that processes aversive information of the pain experience.
This study established a novel approach to investigate neuronal circuits and behaviors responsible for Aβ fiber-mediated neuropathic allodynia. An advantage of this method is the assessment of Aβ fiber-derived neuropathic pain behaviors in awake, freely moving animals without direct contact of the light probe to the skin.
This is in stark contrast to tests using von Frey filaments, brushes, and electrical stimuli. An additional advantage over previous methods is this method can be performed without extensive training. This approach is easier to perform, and we expect it will improve accuracy, and reproducibility between investigators.
Light illumination could also enable stimulation of the ChR2+ Aβ fibers in in vitro and in vivo experimental conditions. A technical limitation of previous methods using filaments and brushes is the inability of mechanical stimuli to activate afferent subpopulations in in vitro studies, such as electrophysiological experiments using spinal slices with dorsal roots.
This model may enable future in vivo and in vitro studies to elucidate the mechanistic underpinnings for Aβ fiber-evoked neuropathic pain.
This study demonstrates for the first time that optogenetic stimulation of non-nociceptive Aβ fibers after PNI produces neuropathic pain-like behaviors with sensory and aversive emotional aspects.
Morphine resistance may correlate with the clinical situation in which neuropathic pain patients are often refractory to treatment. This method could provide a new approach for investigating the mechanisms underlying neuropathic mechanical allodynia with sensory and emotional features, and for developing new drugs to treat neuropathic pain.
Visit eNeuro to read the original article and explore other content. Read other summaries of JNeurosci and eNeuro papers in the Neuronline collection SfN Journals: Research Article Summaries.
Optogenetic Activation of Non-Nociceptive Aβ Fibers Induces Neuropathic Pain-Like Sensory and Emotional Behaviors after Nerve Injury in Rats. Ryoichi Tashima, Keisuke Koga, Misuzu Sekine, Kensho Kanehisa, Yuta Kohro, Keiko Tominaga, Katsuyuki Matsushita, Hidetoshi Tozaki-Saitoh, Yugo Fukazawa, Kazuhide Inoue, Hiromu Yawo, Hidemasa Furue and Makoto Tsuda. eNeuro Feb 2018 5 (1). DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0450-17.2018